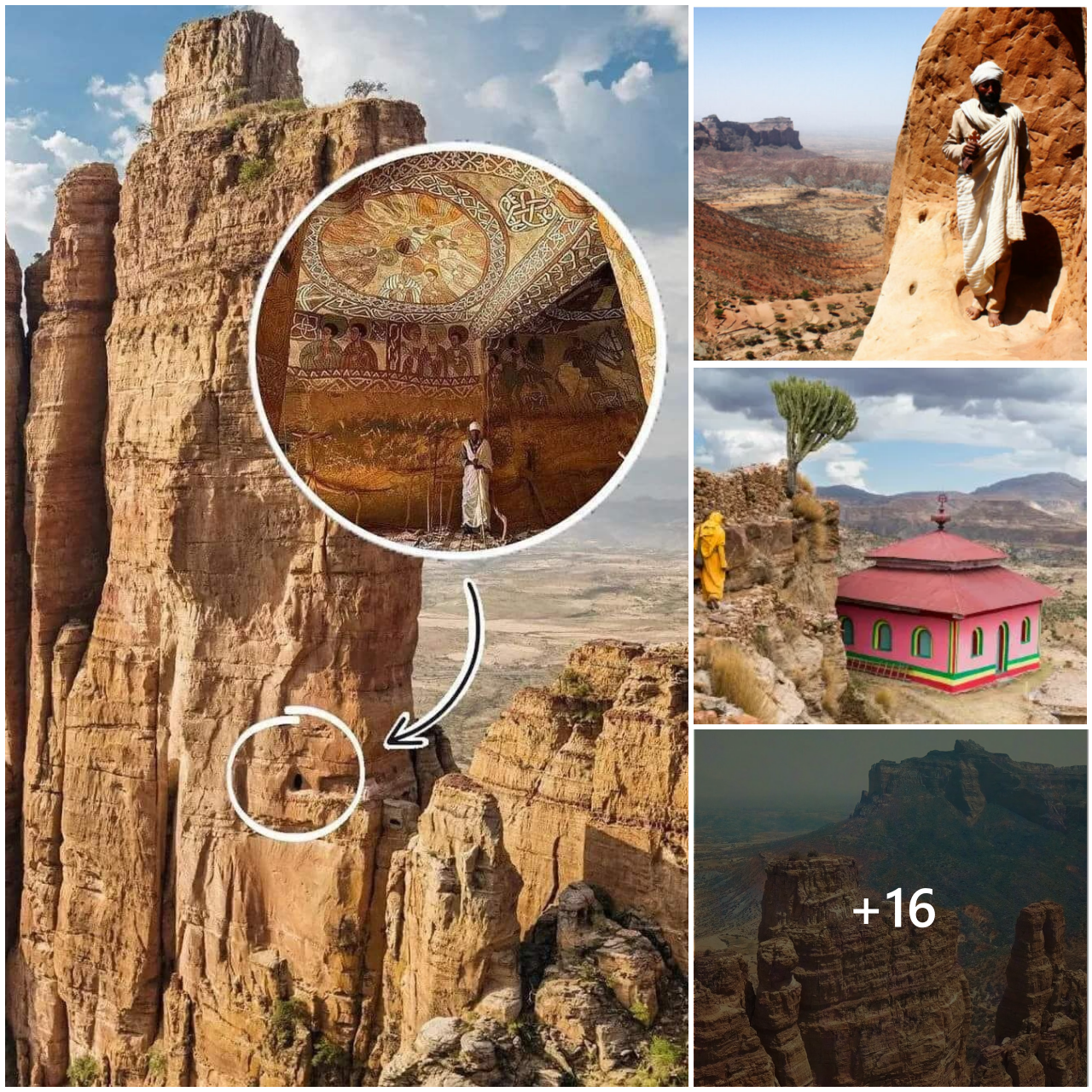
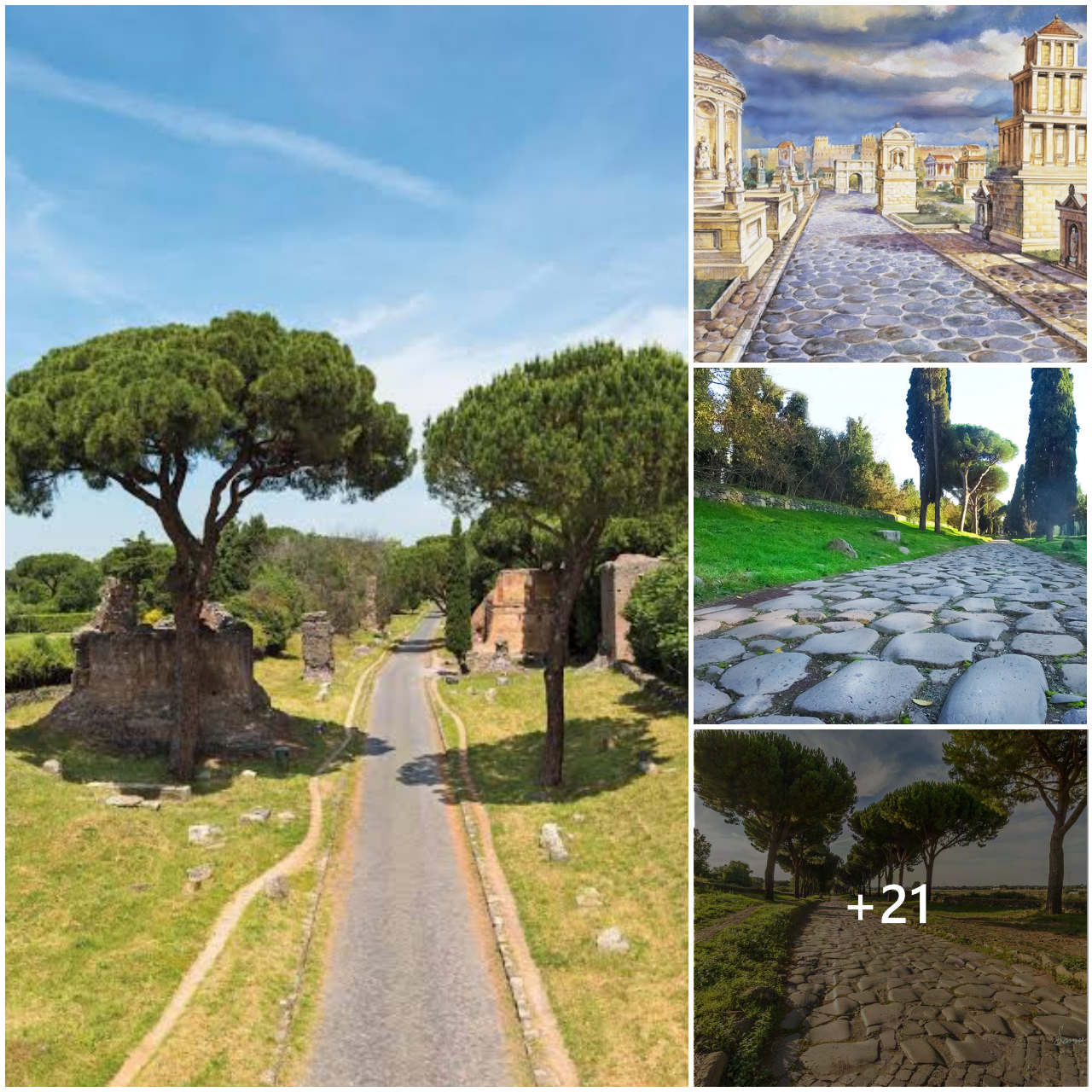
The technology that shows us how ancient Mycenae looked like

The Mycenae, the kingdom of the mythical Agamemnon, which Homer first praised in his poems, is the most important and richest palace center of the Late Bronze Age in Greece. Its name was given to one of the most brilliant civilizations of Greek prehistory, the Mycenaean, and its myths associated with the Homeric epic poems and the great tragedies of the classical era, while inspiring the global intellectual creation and art of the world.
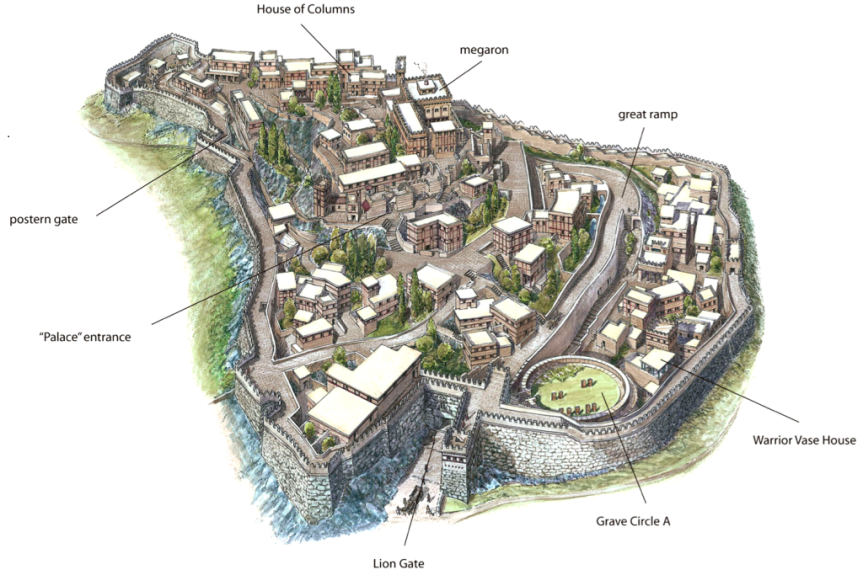
Mycenae was founded between two hills, Profitis Ilias (805 m.) and Sarah (660 m.), on a low hill and had control of the road and sea routes.
Around 1700 BC, aristocratic families appeared, as the use of monumental tombs proves. This development continued at the beginning of the Mycenaean period, around 1600 BC, when a large central building was erected on the top of the hill, a second stone enclosure, the Tomb Circle A, and the first vaulted tombs.
The finds show that the Mycenaean rulers were powerful and participated in a complex trade network with the Mediterranean countries.
Ancient Mycenae 3D reconstruction video:
The reconstruction of the palaces, which are visible today, began around 1350 BC. Then the fortification of the citadel began, in three phases. The first was built with the cyclopean system on the rock. A hundred years later, the fortification shifted to the west and south, and the Lion’s Gate, the monumental entrance with its bastion, was built.
The religious center and the Tomb Circle A, which was formed into an area of ancestor worship, joined the walled area. It is then possible, around 1200 BC, that the vaulted tomb, known as the “Treasure of Atreus” was built. After extensive destruction, possibly by an earthquake, the extension of the walls was built in the north-east of the hill, so that the underground well could be included in the walled area.
Repeated destruction, accompanied by fires, led to the final abandonment of the area around 1100 BC. After the collapse of the palace system, the hill remained sparsely inhabited until the classical period. However, the cyclopean walls of the Mycenaean citadel remained visible over the centuries and were an attraction which many travelers and archeologists did not hesitate to plunder in the 18th and 19th centuries, taking advantage of the indifference and greed of the Turks.
In 1837, after the liberation of Greece, Mycenae came under the patronage of the Athens Archeological Committee, and still makes research in the area.






Why users still use to read news papers when in this technological world everything
is presented on web? I saw similar here: sklep internetowy and also here: e-commerce
My partner and I stumbled over here by a different web address and thought I might check things out.
I like what I see so now i’m following you.
Look forward to going over your web page again. I saw similar here: sklep
and also here: sklep internetowy