Dinosaurs actually did not become completely extinct, their descendants still shared the earth with humans. They fly above our heads, they pick up food from the ground, you see them everywhere and they appear on the dinner table. Descendants of some dinosaurs survived the mass extinction to continue to evolve and become birds.
Dinosaurs did not become completely extinct
The age of dinosaurs began in the Triassic period (243 – 233.23 million years ago) and flourished in the Jurassic period (201.3 – 145 million years ago) before ending with the great extinction at the end of the Cretaceous period. White as we all know 66 million years ago.
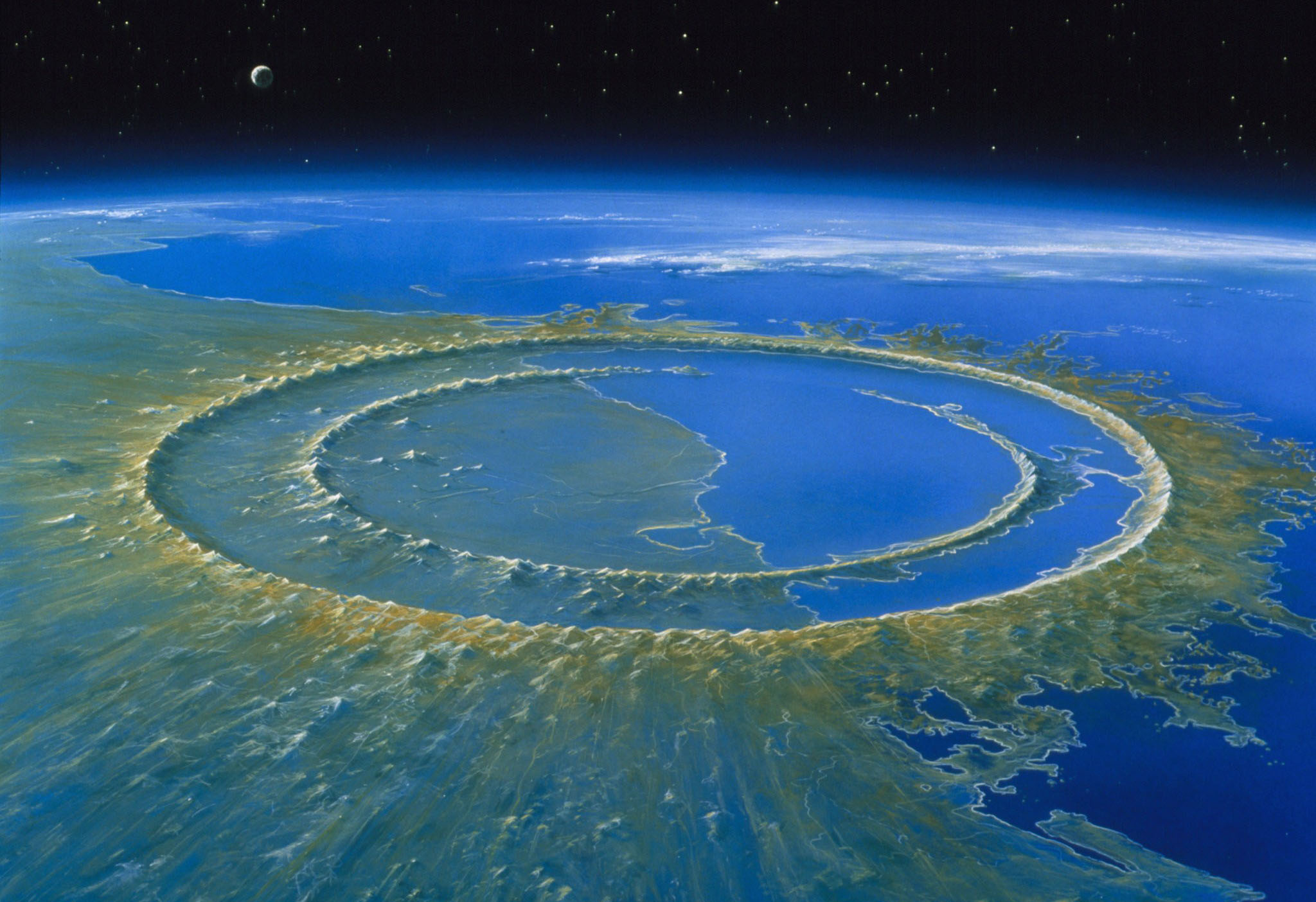
The late Cretaceous meteorite impact and the volcanic eruptions it followed released huge amounts of ash into the atmosphere. Smog obscures the sun, making the earth colder, creating a nuclear winter effect that lasts for decades on a global scale. Plants cannot survive, leading to the extinction of herbivores. “On the plate” first were the large thunder lizards weighing dozens of tons that needed too much food, followed by the large carnivores that starved to death because there was no longer enough meat to feed them. The smaller the animals, the less food they need, the better their chances of survival. They dig into the ground, hide in dead forests or hide in the deep ocean to survive and wait for the end of the world to pass.
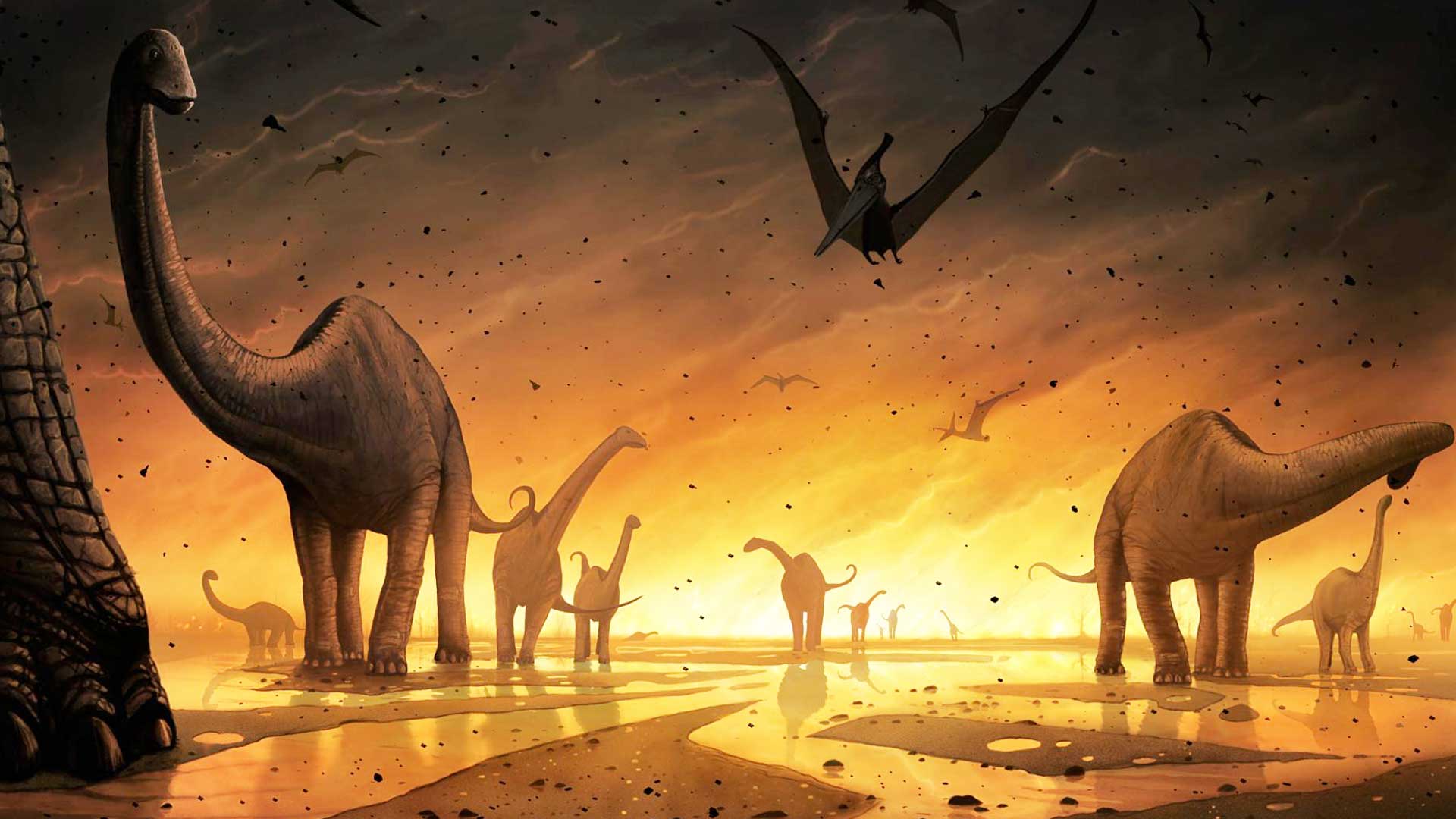

That terrible event wiped out three-quarters of animal species. All living species today are descendants of one-fourth of the living species that resiliently survived. Including the adorable little descendants of some dinosaurs, living with us in the modern world – birds.
Birds are descendants of theropod dinosaurs (Theropoda).
According to evidence collected throughout the history of Mesozoic paleontology, birds are descendants of several species of theropod dinosaurs. The most notable of these is the results of a research project from paleontologists at the University of Adelaide (Australia) published in Science magazine in 2014.
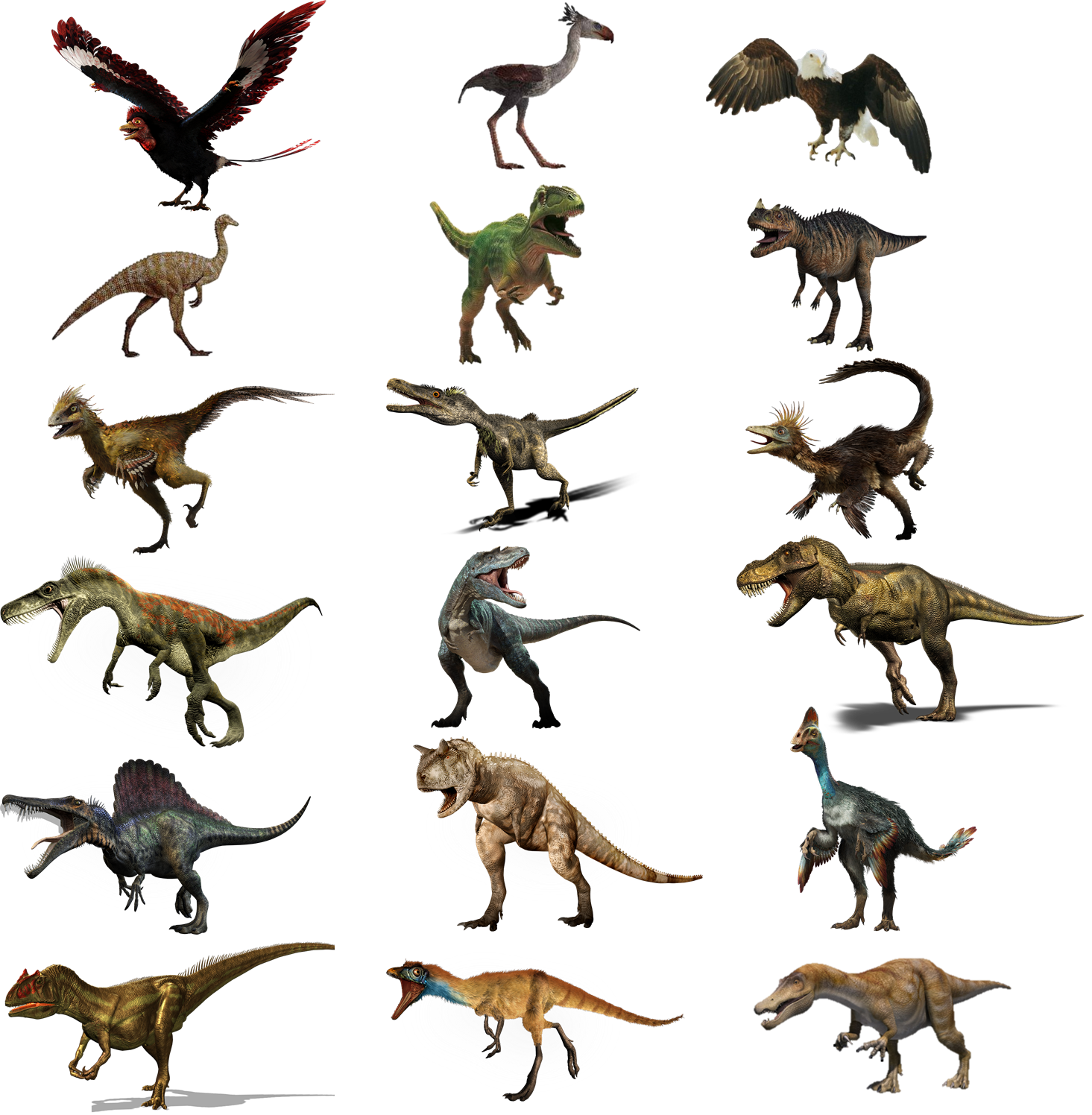
In this research, they analyzed and compared more than 1,500 anatomical features of many dinosaur species over a 50 million year evolutionary process (from about 200 million years ago to 150 million years ago) to create their family tree. Researchers used a variety of complex mathematical models to track adaptations and changes in body size over time across dinosaur branches in the evolutionary tree. As a result, they found out that the exact origin of modern birds is from some species of theropod dinosaurs.
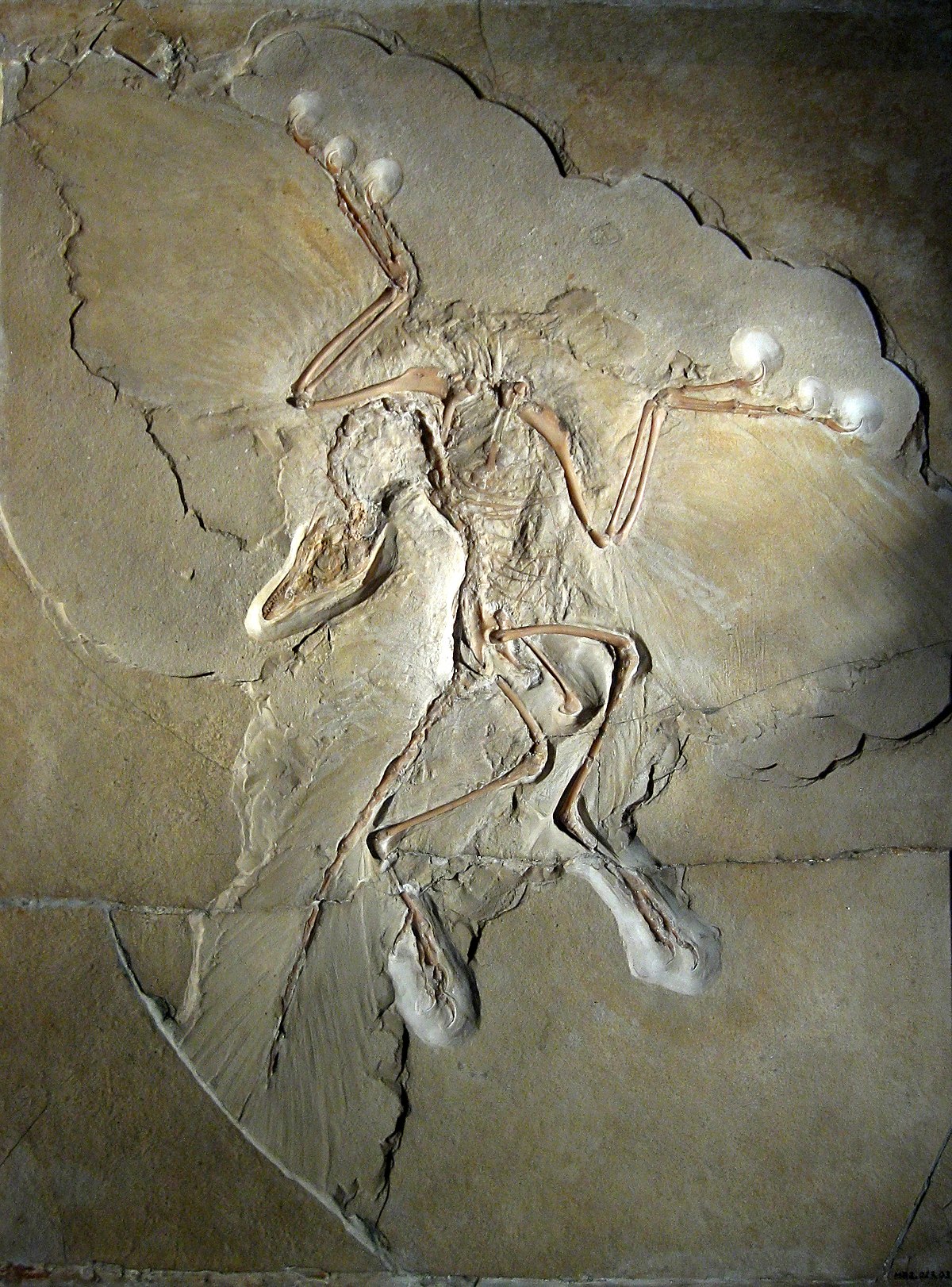

During those 50 million years, their average weight decreased from 163kg to only 0.8kg, and the species Archeopteryx (ancestral bird) appeared. This species is considered a transition between dinosaurs and modern birds, they have feathers, light bodies, eat meat and can fly.
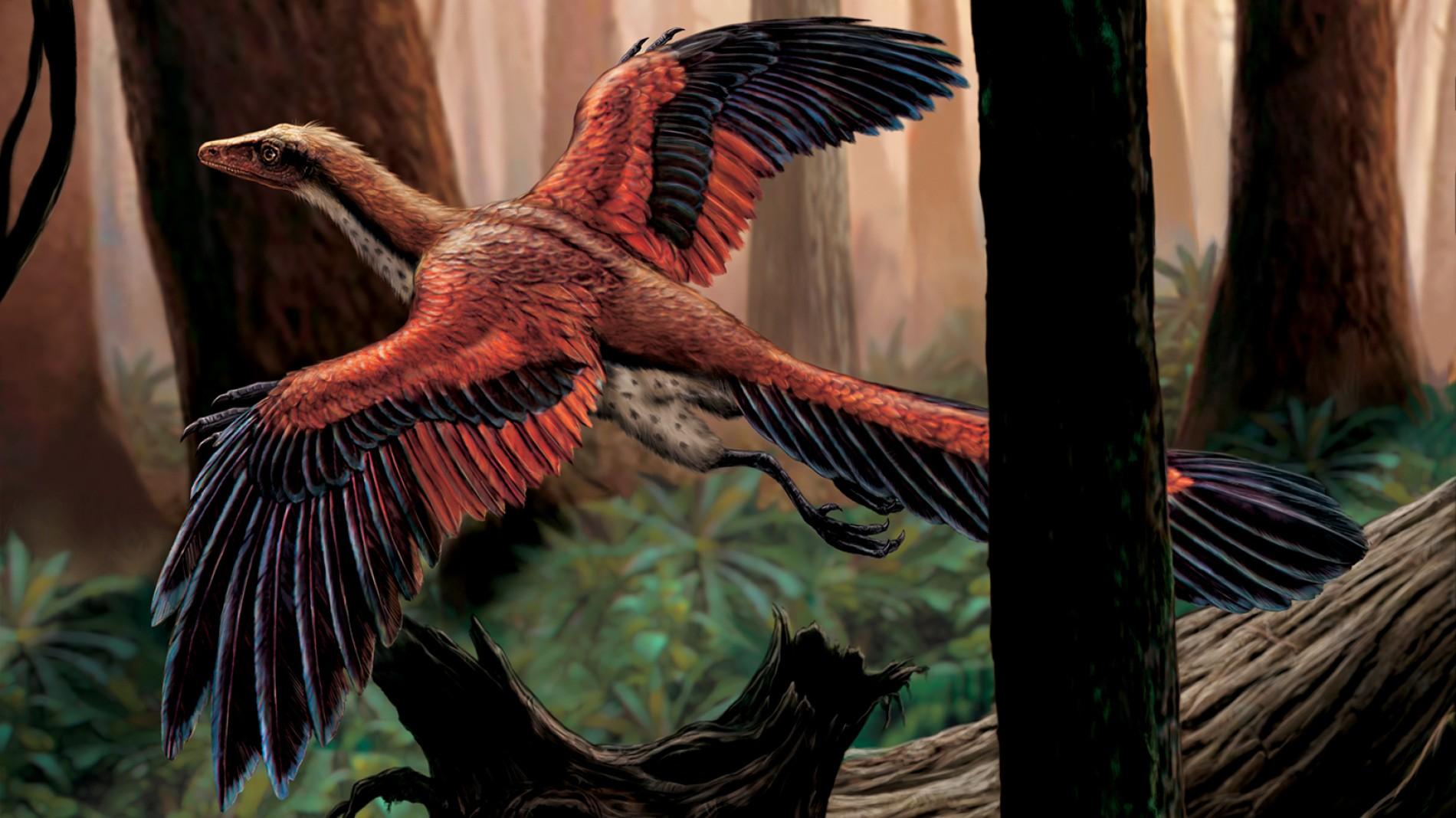

As for why they got smaller and developed feathers, University of Adelaide paleontologists say that dinosaurs that were small, could climb and had feathers would have had the most advantages. determined. For example, they can climb trees to hide from enemies, jump-glide better, and access food sources that big guys can’t reach. Birds then evolved for tens of millions of years, sharing the sky with pterosaurs until they overcame the mass extinction event along with human ancestors and many small, resilient creatures. another strength.
“Modern Dinosaurs”
Today there are about 10,000 bird species in the world. So instead of saying that dinosaurs are extinct, do you think more positively for them, that there are 10,000 species of modern dinosaurs sharing this earth with us and many other creatures? This means that things like chickens, ducks, storks, seagulls, ostriches, penguins… all have heroic ancestors.

*More information for those of you who are unfamiliar with theropods: They are actually quite famous in movies. From the giant T-rex to the two-horned Carnotaurus or the agile and cunning Velociraptors, they all belong to the group of theropod dinosaurs.





