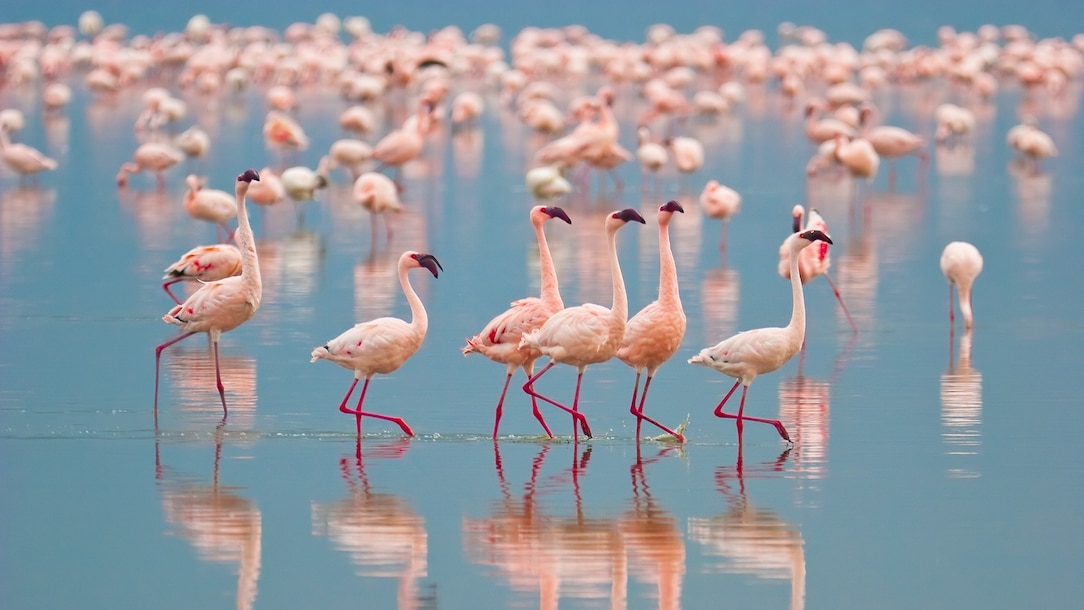
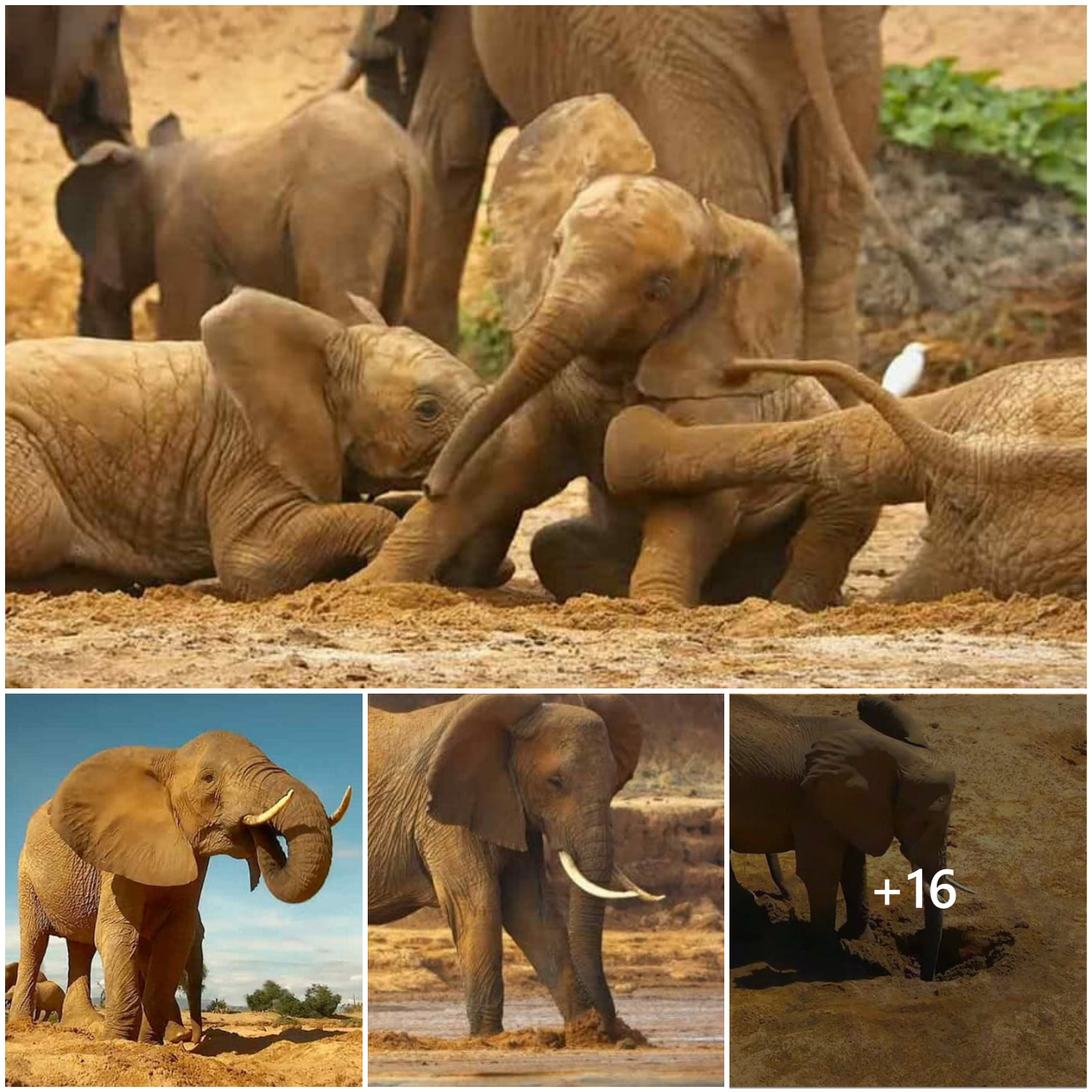
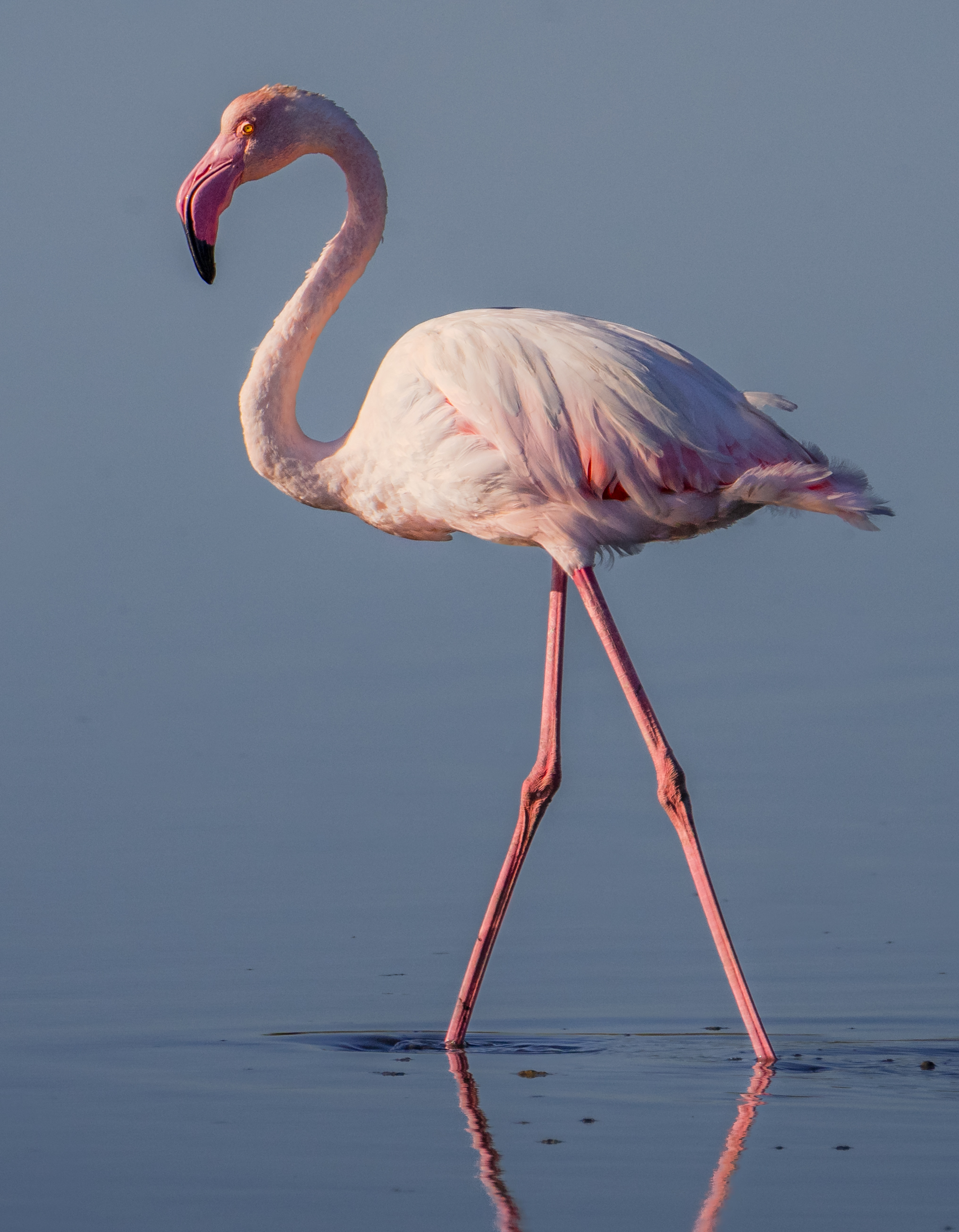
A flamingo’s color varies depending on what it eats.

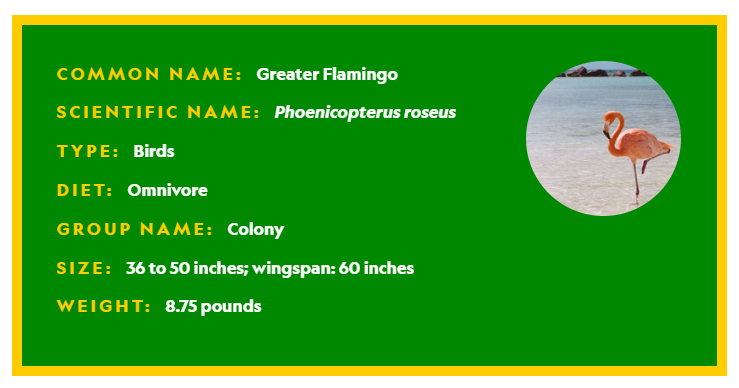
- Common Name: Greater Flamingo
- Scientific Name: Phoenicopterus roseus
- Type: Birds
- Diet: Omnivore
- Group Name: Colony
- Size: 36 to 50 inches; wingspan: 60 inches
- Weight: 8.75 pounds
When a flamingo spots potential dinner—favorite foods include shrimp, snails, and plantlike water organisms called algae—it plunges its head into the water, twists it upside down, and scoops the fish using its upper beak like a shovel. They are able to “run” on water, thanks to their webbed feet, to gain speed before lifting up into the sky.

Flamingos build nests that look like mounds of mud along waterways. At the top of the mound, in a shallow hole, the female lays one egg. The parents take turns sitting on the egg to keep it warm. After about 30 days, the egg hatches.
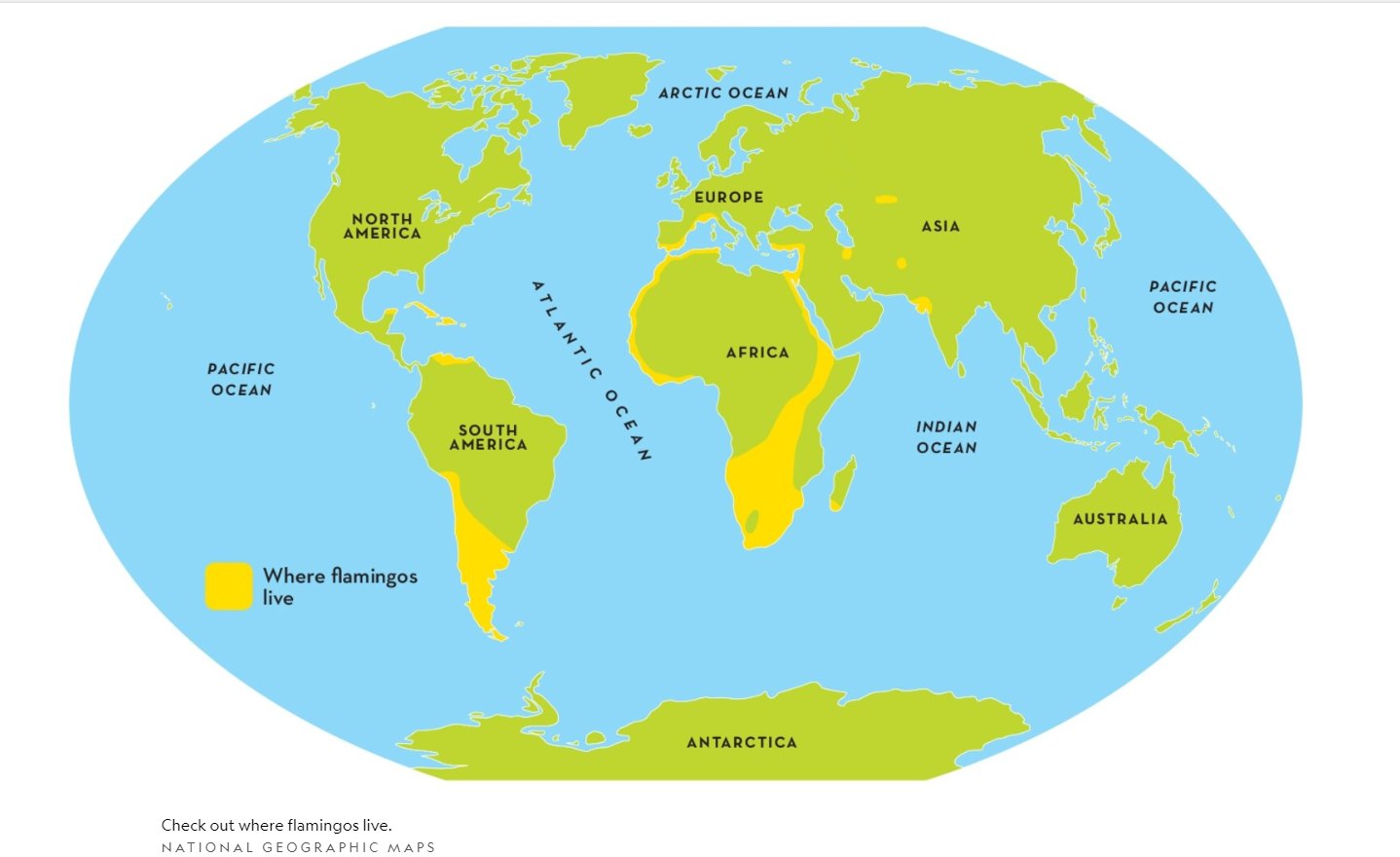
Check out where flamingos live
Please be respectful of copyright. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Flamingo young are born white, with soft, downy feathers and a straight bill. The bill gradually curves downward as the flamingo matures. Both parents take care of the newborn flamingo, feeding it a fluid produced in their digestive systems. The young leave the nest after about five days to join other young flamingos in small groups, returning to the parents for food. The parents identify their chick by its voice. After about three weeks, the adults herd young flamingos into large groups called crèches where they start to look for food on their own.

Most flamingo species are not endangered, although the Andean flamingo is listed as vulnerable, and the Chilean, Lesser, and Puna flamingos are near threatened.






